Chickenpox
Published: 18 Jun 2025
ICD9: 052 ICD10: B01 ICD11: 1E90
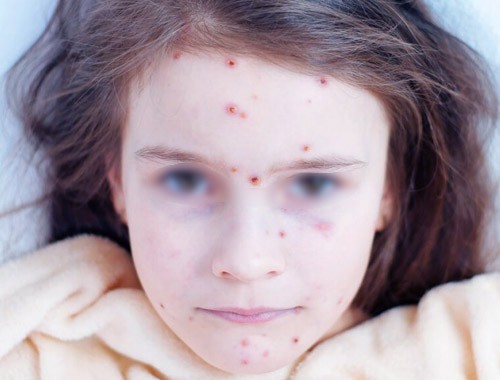
Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV).
It's characterized by an itchy, blister-like rash on the skin.
Here's a breakdown of key aspects:
![]() Cause: Varicella-zoster virus (VZV)
Cause: Varicella-zoster virus (VZV)
![]() Symptoms:
Symptoms:![]()

![]() Itchy rash with small, fluid-filled blisters that eventually scab over.
Itchy rash with small, fluid-filled blisters that eventually scab over.![]()

![]() Fever
Fever![]()

![]() Fatigue
Fatigue![]()

![]() Headache
Headache![]()

![]() Loss of appetite
Loss of appetite
![]() Transmission:
Transmission:![]()

![]() Direct contact with the blisters.
Direct contact with the blisters.![]()

![]() Airborne spread through coughing or sneezing.
Airborne spread through coughing or sneezing.
![]() Contagious Period:
Contagious Period:![]()

![]() One to two days *before* the rash appears until all blisters have crusted over.
One to two days *before* the rash appears until all blisters have crusted over.
![]() Prevention:
Prevention:![]()

![]() Varicella vaccine (two doses are recommended)
Varicella vaccine (two doses are recommended)
![]() Treatment:
Treatment:![]()

![]() Usually symptomatic relief, such as:
Usually symptomatic relief, such as:![]()

![]() Calamine lotion to relieve itching.
Calamine lotion to relieve itching.![]()

![]() Antihistamines to relieve itching.
Antihistamines to relieve itching.![]()

![]() Acetaminophen to reduce fever.
Acetaminophen to reduce fever.![]()

![]() Antiviral medications (like acyclovir) may be prescribed, especially for adults, teenagers, or people with weakened immune systems, but are most effective if started within 24 hours of the rash appearing.
Antiviral medications (like acyclovir) may be prescribed, especially for adults, teenagers, or people with weakened immune systems, but are most effective if started within 24 hours of the rash appearing.
![]() Complications:
Complications:![]()

![]() Skin infections (from scratching)
Skin infections (from scratching)![]()

![]() Pneumonia
Pneumonia![]()

![]() Encephalitis (inflammation of the brain)
Encephalitis (inflammation of the brain)![]()

![]() In rare cases, death
In rare cases, death
![]() Shingles:
Shingles:![]()

![]() After someone has chickenpox, the virus can lie dormant in the nerve cells. It can reactivate later in life and cause shingles, a painful rash in a localized area.
After someone has chickenpox, the virus can lie dormant in the nerve cells. It can reactivate later in life and cause shingles, a painful rash in a localized area.
Important Considerations:
![]() Vaccination is key: The chickenpox vaccine is very effective at preventing the disease or reducing the severity of symptoms if a breakthrough infection occurs.
Vaccination is key: The chickenpox vaccine is very effective at preventing the disease or reducing the severity of symptoms if a breakthrough infection occurs.
![]() Consult a doctor: If you suspect you or your child has chickenpox, see a doctor for diagnosis and guidance.
Consult a doctor: If you suspect you or your child has chickenpox, see a doctor for diagnosis and guidance.
![]() Avoid scratching: Scratching can lead to secondary bacterial infections.
Avoid scratching: Scratching can lead to secondary bacterial infections.
![]() Isolation: Stay home from school or work to prevent spreading the virus until all blisters have crusted over.
Isolation: Stay home from school or work to prevent spreading the virus until all blisters have crusted over.
![]() Pregnancy: Chickenpox during pregnancy can be dangerous for the fetus. If a pregnant woman is not immune and is exposed, she should see a doctor immediately.
Pregnancy: Chickenpox during pregnancy can be dangerous for the fetus. If a pregnant woman is not immune and is exposed, she should see a doctor immediately.
In summary, chickenpox is a common, highly contagious viral illness characterized by a distinctive rash. Vaccination is the best way to prevent it, and treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing complications.