Coronary Artery Disease Atherosclerosis (Arteriosclerosis)
Published: 18 Jun 2025
ICD9: 414.01 ICD10: I25.10 ICD11: BA80
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is a specific type of heart disease that is primarily caused by atherosclerosis, which is a form of arteriosclerosis.
Let's break down what each of these terms means:
![]() Arteriosclerosis: This is a general term referring to the hardening and thickening of the arteries. Think of it as an umbrella term. Arteries are the blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood away from your heart to the rest of your body. When they become stiff and less elastic, it restricts blood flow.
Arteriosclerosis: This is a general term referring to the hardening and thickening of the arteries. Think of it as an umbrella term. Arteries are the blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood away from your heart to the rest of your body. When they become stiff and less elastic, it restricts blood flow.
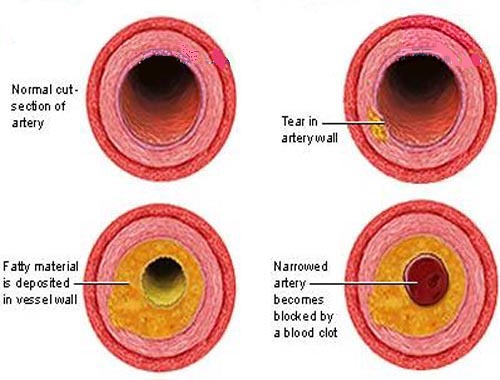
![]() Atherosclerosis: This is the most common type of arteriosclerosis. It's a specific process where plaque builds up inside the arteries. This plaque is made up of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances found in the blood. Over time, this plaque hardens and narrows the arteries, further restricting blood flow.
Atherosclerosis: This is the most common type of arteriosclerosis. It's a specific process where plaque builds up inside the arteries. This plaque is made up of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances found in the blood. Over time, this plaque hardens and narrows the arteries, further restricting blood flow.
![]() Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): This occurs when atherosclerosis affects the coronary arteries. These are the arteries that supply blood *directly to the heart muscle itself*. When these arteries become narrowed or blocked by plaque, the heart muscle doesn't get enough oxygen-rich blood, which can lead to chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, heart attack, and other serious problems.
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): This occurs when atherosclerosis affects the coronary arteries. These are the arteries that supply blood *directly to the heart muscle itself*. When these arteries become narrowed or blocked by plaque, the heart muscle doesn't get enough oxygen-rich blood, which can lead to chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, heart attack, and other serious problems.
In simpler terms:
Imagine your arteries are pipes carrying water.
![]() Arteriosclerosis is like the pipes becoming stiff and less flexible with age.
Arteriosclerosis is like the pipes becoming stiff and less flexible with age.
![]() Atherosclerosis is like gunk (plaque) building up inside those pipes, narrowing the space and making it harder for water to flow through.
Atherosclerosis is like gunk (plaque) building up inside those pipes, narrowing the space and making it harder for water to flow through.
![]() Coronary Artery Disease is when that gunk builds up specifically in the pipes that feed water *to the pump itself* (your heart).
Coronary Artery Disease is when that gunk builds up specifically in the pipes that feed water *to the pump itself* (your heart).
Key Points to Remember:
![]() CAD is a major health problem and a leading cause of death worldwide.
CAD is a major health problem and a leading cause of death worldwide.
![]() The main culprit behind CAD is atherosclerosis.
The main culprit behind CAD is atherosclerosis.
![]() Atherosclerosis is a form of arteriosclerosis.
Atherosclerosis is a form of arteriosclerosis.
![]() The buildup of plaque in the coronary arteries restricts blood flow to the heart muscle, leading to various complications.
The buildup of plaque in the coronary arteries restricts blood flow to the heart muscle, leading to various complications.
Risk factors for CAD include:
![]() High cholesterol
High cholesterol
![]() High blood pressure
High blood pressure
![]() Smoking
Smoking
![]() Diabetes
Diabetes
![]() Obesity
Obesity
![]() Family history of heart disease
Family history of heart disease
![]() Lack of physical activity
Lack of physical activity
![]() Unhealthy diet
Unhealthy diet
![]() Older age
Older age
![]() Stress
Stress
Understanding the relationship between arteriosclerosis, atherosclerosis, and CAD is crucial for preventing and managing this serious condition. Lifestyle changes and medical treatments can help slow the progression of atherosclerosis and reduce the risk of complications from CAD. It's best to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and management strategies.