Endocarditis
Published: 18 Jun 2025
ICD9: 424.90 ICD10: I38 ICD11: BB4Z
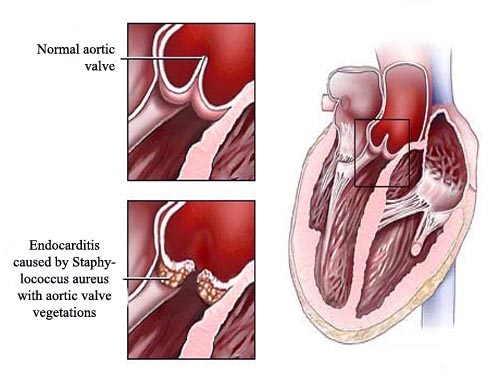
Endocarditis is an infection of the inner lining of your heart chambers and heart valves (the endocardium).
It happens when bacteria, fungi, or other germs from another part of your body, such as your mouth, travel through your bloodstream and attach to damaged areas in your heart.
Here's a breakdown:
![]() What's affected: The endocardium, which includes the heart valves.
What's affected: The endocardium, which includes the heart valves.
![]() Cause: Infection by bacteria, fungi, or other germs. These germs typically enter the bloodstream from elsewhere in the body.
Cause: Infection by bacteria, fungi, or other germs. These germs typically enter the bloodstream from elsewhere in the body.
![]() How it happens: Germs attach to damaged areas of the heart. Damage can be caused by congenital heart defects, damaged heart valves, or implanted devices.
How it happens: Germs attach to damaged areas of the heart. Damage can be caused by congenital heart defects, damaged heart valves, or implanted devices.
![]() Consequences: Endocarditis can damage your heart valves, lead to serious complications like heart failure, stroke, and even death.
Consequences: Endocarditis can damage your heart valves, lead to serious complications like heart failure, stroke, and even death.
Key points to remember:
![]() Seriousness: Endocarditis is a serious condition that requires prompt treatment.
Seriousness: Endocarditis is a serious condition that requires prompt treatment.
![]() Vulnerable individuals: People with certain heart conditions are at higher risk.
Vulnerable individuals: People with certain heart conditions are at higher risk.
![]() Prevention: Good dental hygiene and preventive antibiotics (in some cases) are important for high-risk individuals.
Prevention: Good dental hygiene and preventive antibiotics (in some cases) are important for high-risk individuals.
Symptoms can include:
![]() Flu-like symptoms (fever, chills, fatigue)
Flu-like symptoms (fever, chills, fatigue)
![]() New or changed heart murmur
New or changed heart murmur
![]() Shortness of breath
Shortness of breath
![]() Night sweats
Night sweats
![]() Swelling in your feet, legs, or abdomen
Swelling in your feet, legs, or abdomen
![]() Unexplained weight loss
Unexplained weight loss
![]() Small, painful nodules on your fingers or toes (Osler's nodes)
Small, painful nodules on your fingers or toes (Osler's nodes)
![]() Tiny purple or red spots on the skin (petechiae) or in the whites of the eyes
Tiny purple or red spots on the skin (petechiae) or in the whites of the eyes
If you think you might have endocarditis, see a doctor immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment with antibiotics or, in some cases, surgery, are crucial for a good outcome.
![]() Disclaimer: This information is for general knowledge only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of any medical condition.*
Disclaimer: This information is for general knowledge only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of any medical condition.*