Felty syndrome
Published: 18 Jun 2025
ICD9: 714.1 ICD10: M05.00 ICD11: FA20.0
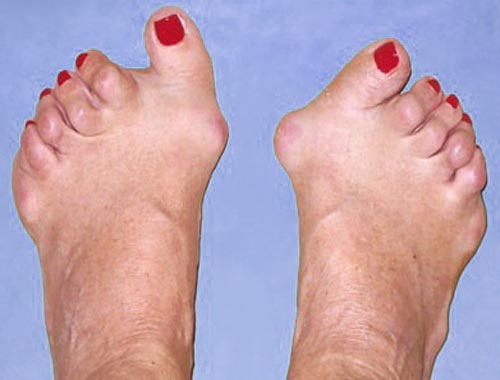
Felty syndrome is a rare and serious complication of rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
It's characterized by a specific triad of conditions:
![]() Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): A chronic autoimmune disease that causes inflammation and pain in the joints. This is the underlying condition in Felty syndrome.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): A chronic autoimmune disease that causes inflammation and pain in the joints. This is the underlying condition in Felty syndrome.
![]() Splenomegaly: An enlarged spleen. The spleen is an organ in the upper left abdomen that filters blood and helps fight infections.
Splenomegaly: An enlarged spleen. The spleen is an organ in the upper left abdomen that filters blood and helps fight infections.
![]() Neutropenia: A low count of neutrophils in the blood. Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell that are important for fighting off bacterial infections. This makes people with Felty syndrome more susceptible to infections.
Neutropenia: A low count of neutrophils in the blood. Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell that are important for fighting off bacterial infections. This makes people with Felty syndrome more susceptible to infections.
In simpler terms:
Felty syndrome is when someone with rheumatoid arthritis also develops an enlarged spleen and a low white blood cell count, making them more prone to infections.
Key Points about Felty Syndrome:
![]() Rarity: It affects less than 1% of people with RA.
Rarity: It affects less than 1% of people with RA.
![]() Severity: It can increase the risk of serious infections and other complications.
Severity: It can increase the risk of serious infections and other complications.
![]() Cause: The exact cause is not fully understood, but it involves the immune system attacking neutrophils and potentially the spleen.
Cause: The exact cause is not fully understood, but it involves the immune system attacking neutrophils and potentially the spleen.
![]() Symptoms (besides those defining the syndrome):
Symptoms (besides those defining the syndrome):![]()

![]() Fatigue
Fatigue![]()

![]() Pale skin
Pale skin![]()

![]() Mouth sores
Mouth sores![]()

![]() Leg ulcers
Leg ulcers![]()

![]() Increased susceptibility to infections (especially bacterial)
Increased susceptibility to infections (especially bacterial)
![]() Diagnosis: Diagnosed based on the presence of the triad (RA, splenomegaly, neutropenia) and sometimes confirmed with a bone marrow biopsy or other tests.
Diagnosis: Diagnosed based on the presence of the triad (RA, splenomegaly, neutropenia) and sometimes confirmed with a bone marrow biopsy or other tests.
![]() Treatment: Treatment focuses on managing the rheumatoid arthritis and addressing the neutropenia. Options include:
Treatment: Treatment focuses on managing the rheumatoid arthritis and addressing the neutropenia. Options include:![]()

![]() RA medications (DMARDs, biologics)
RA medications (DMARDs, biologics)![]()

![]() Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) to boost neutrophil production
Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) to boost neutrophil production![]()

![]() Splenectomy (removal of the spleen) in severe cases, though this is usually a last resort due to risks.
Splenectomy (removal of the spleen) in severe cases, though this is usually a last resort due to risks.
If someone has rheumatoid arthritis and experiences frequent infections, fatigue, or other unusual symptoms, they should see their doctor to be evaluated for Felty syndrome. Early diagnosis and treatment are important to prevent complications.