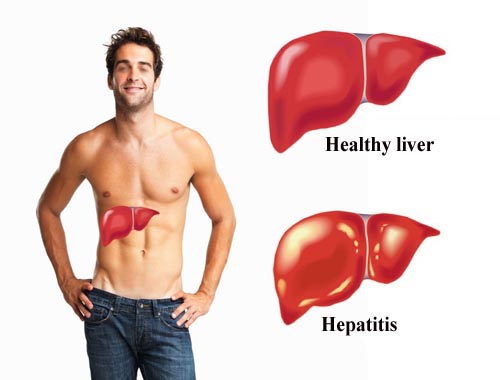
Hepatitis
Published: 18 Jun 2025
ICD9: 573.3 ICD10: K71.6 ICD11: 1E50
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver.
It can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
![]() Viral infections: This is the most common cause of hepatitis. The most common types of viral hepatitis are hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C. Other viruses can also cause hepatitis, such as the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and cytomegalovirus (CMV).
Viral infections: This is the most common cause of hepatitis. The most common types of viral hepatitis are hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C. Other viruses can also cause hepatitis, such as the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and cytomegalovirus (CMV).
![]() Alcohol abuse: Excessive alcohol consumption can damage the liver and lead to alcoholic hepatitis.
Alcohol abuse: Excessive alcohol consumption can damage the liver and lead to alcoholic hepatitis.
![]() Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): This condition is characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver and can lead to inflammation and damage.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): This condition is characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver and can lead to inflammation and damage.
![]() Autoimmune diseases: In autoimmune hepatitis, the body's immune system attacks the liver.
Autoimmune diseases: In autoimmune hepatitis, the body's immune system attacks the liver.
![]() Medications: Certain medications can cause drug-induced hepatitis.
Medications: Certain medications can cause drug-induced hepatitis.
![]() Toxins: Exposure to certain toxins can damage the liver and cause hepatitis.
Toxins: Exposure to certain toxins can damage the liver and cause hepatitis.
The symptoms of hepatitis can vary depending on the cause and severity of the inflammation. Some people with hepatitis may not have any symptoms, while others may experience:
![]() Fatigue
Fatigue
![]() Flu-like symptoms
Flu-like symptoms
![]() Loss of appetite
Loss of appetite
![]() Nausea and vomiting
Nausea and vomiting
![]() Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain
![]() Dark urine
Dark urine
![]() Pale stools
Pale stools
![]() Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
Hepatitis can be acute (short-term) or chronic (long-term). Acute hepatitis usually resolves on its own, but chronic hepatitis can lead to serious complications such as liver cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer.
Diagnosis of hepatitis typically involves blood tests to check liver function and detect the presence of viral infections or antibodies. In some cases, a liver biopsy may be necessary to determine the extent of liver damage.
Treatment for hepatitis depends on the cause of the inflammation. Viral hepatitis can be treated with antiviral medications. Autoimmune hepatitis is treated with immunosuppressants. Alcoholic hepatitis requires abstinence from alcohol.
If you think you may have hepatitis, it is important to see a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.