Hepatitis A
Published: 18 Jun 2025
ICD9: 070.1 ICD10: B15.9 ICD11: 1E50.0
Hepatitis A is a highly contagious liver infection caused by the hepatitis A virus (HAV).
Here's a breakdown:
What it is:
![]() Infection of the liver: The virus inflames and damages the liver.
Infection of the liver: The virus inflames and damages the liver.
![]() Caused by a virus: Specifically, the Hepatitis A virus (HAV).
Caused by a virus: Specifically, the Hepatitis A virus (HAV).
![]() Usually acute (short-term): Most people recover completely within a few weeks to months without lasting liver damage. Chronic hepatitis A is very rare.
Usually acute (short-term): Most people recover completely within a few weeks to months without lasting liver damage. Chronic hepatitis A is very rare.
How it spreads (Transmission):
![]() Fecal-oral route: This is the primary way it spreads. The virus is shed in the stool of infected people.
Fecal-oral route: This is the primary way it spreads. The virus is shed in the stool of infected people.![]()

![]() Contaminated food or water: This is a common source, especially when food is handled by an infected person who doesn't wash their hands properly. Shellfish from contaminated water can also be a source.
Contaminated food or water: This is a common source, especially when food is handled by an infected person who doesn't wash their hands properly. Shellfish from contaminated water can also be a source.![]()

![]() Close personal contact: Touching contaminated surfaces and then touching your mouth, or having close contact with an infected person.
Close personal contact: Touching contaminated surfaces and then touching your mouth, or having close contact with an infected person.![]()

![]() Sexual contact: Particularly oral-anal contact.
Sexual contact: Particularly oral-anal contact.
Symptoms:
Symptoms can vary, but commonly include:
![]() Fatigue
Fatigue
![]() Nausea and vomiting
Nausea and vomiting
![]() Abdominal pain (especially in the upper right quadrant)
Abdominal pain (especially in the upper right quadrant)
![]() Loss of appetite
Loss of appetite
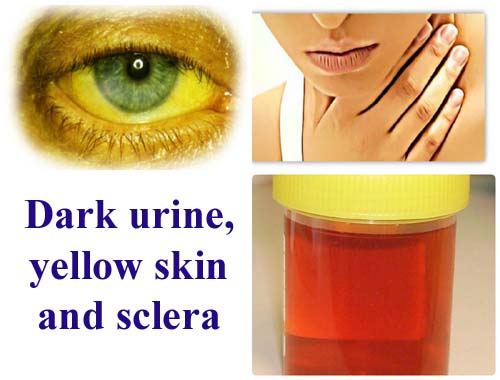
![]() Dark urine
Dark urine
![]() Clay-colored stools
Clay-colored stools
![]() Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
![]() Fever
Fever
![]() Some people, especially children, may have no symptoms.
Some people, especially children, may have no symptoms.
Diagnosis:
![]() Blood tests: A blood test can detect the presence of antibodies to the hepatitis A virus, indicating infection.
Blood tests: A blood test can detect the presence of antibodies to the hepatitis A virus, indicating infection.
Treatment:
![]() No specific treatment: Hepatitis A usually resolves on its own.
No specific treatment: Hepatitis A usually resolves on its own.
![]() Supportive care: Rest, adequate hydration, and avoiding alcohol and medications that can harm the liver are important. Anti-nausea medication may be prescribed.
Supportive care: Rest, adequate hydration, and avoiding alcohol and medications that can harm the liver are important. Anti-nausea medication may be prescribed.
Prevention:
![]() Vaccination: The hepatitis A vaccine is highly effective and is recommended for:
Vaccination: The hepatitis A vaccine is highly effective and is recommended for:![]()

![]() Children
Children![]()

![]() Travelers to areas where hepatitis A is common
Travelers to areas where hepatitis A is common![]()

![]() People with chronic liver disease
People with chronic liver disease![]()

![]() Men who have sex with men
Men who have sex with men![]()

![]() People who use illicit drugs
People who use illicit drugs![]()

![]() People who work in food service or healthcare
People who work in food service or healthcare
![]() Good hygiene:
Good hygiene:![]()

![]() Wash hands thoroughly: Especially after using the toilet, before preparing or eating food, and after changing diapers.
Wash hands thoroughly: Especially after using the toilet, before preparing or eating food, and after changing diapers.![]()

![]() Proper food handling: Cook food to safe temperatures.
Proper food handling: Cook food to safe temperatures.![]()

![]() Drink safe water: If traveling in areas where water quality is questionable, drink bottled or boiled water.
Drink safe water: If traveling in areas where water quality is questionable, drink bottled or boiled water.
![]() Avoid risky behaviors: Practicing safe sex.
Avoid risky behaviors: Practicing safe sex.
Key Differences from other Hepatitis Viruses:
![]() Hepatitis A: Acute, usually resolves on its own, preventable with a vaccine, doesn't cause chronic liver disease.
Hepatitis A: Acute, usually resolves on its own, preventable with a vaccine, doesn't cause chronic liver disease.
![]() Hepatitis B and C: Can become chronic, can lead to serious liver damage (cirrhosis, liver cancer), have different routes of transmission (primarily blood and body fluids). While there is a vaccine for Hepatitis B, there isn't one for Hepatitis C.
Hepatitis B and C: Can become chronic, can lead to serious liver damage (cirrhosis, liver cancer), have different routes of transmission (primarily blood and body fluids). While there is a vaccine for Hepatitis B, there isn't one for Hepatitis C.
In summary: Hepatitis A is a contagious liver infection, typically mild and self-limiting, that is preventable through vaccination and good hygiene. It is important to understand how it spreads to protect yourself and others. If you think you may have been exposed to hepatitis A or are experiencing symptoms, see a doctor.