Melanoma, Skin cancer
Published: 18 Jun 2025
ICD9: 172.3 ICD10: C43.9 ICD11: 2C30
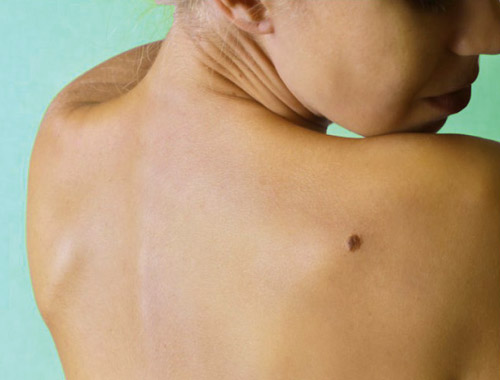
Melanoma is the most serious type of skin cancer.
It develops when melanocytes (the cells that produce melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color) become cancerous.
Here's a breakdown of what that means and why it's important:
Key Facts about Melanoma:
![]() Origin: Arises from melanocytes, which are found primarily in the skin but also in other parts of the body, like the eyes and, rarely, internal organs.
Origin: Arises from melanocytes, which are found primarily in the skin but also in other parts of the body, like the eyes and, rarely, internal organs.
![]() Cause: The primary cause is exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight or tanning beds. However, genetics and other factors also play a role.
Cause: The primary cause is exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight or tanning beds. However, genetics and other factors also play a role.
![]() Appearance: Melanomas can appear in many different forms. They can be:
Appearance: Melanomas can appear in many different forms. They can be:![]()

![]() A new, unusual growth on the skin.
A new, unusual growth on the skin.![]()

![]() A change in an existing mole (size, shape, color, texture).
A change in an existing mole (size, shape, color, texture).![]()

![]() A dark spot under a fingernail or toenail.
A dark spot under a fingernail or toenail.
![]() The "ABCDEs" of Melanoma: A helpful guide for recognizing potentially cancerous moles:
The "ABCDEs" of Melanoma: A helpful guide for recognizing potentially cancerous moles:![]()

![]() Asymmetry: One half of the mole doesn't match the other half.
Asymmetry: One half of the mole doesn't match the other half.![]()

![]() Border: The edges are irregular, notched, or blurred.
Border: The edges are irregular, notched, or blurred.![]()

![]() Color: The mole has uneven colors (black, brown, tan, red, white, blue).
Color: The mole has uneven colors (black, brown, tan, red, white, blue).![]()

![]() Diameter: The mole is larger than 6 millimeters (about 1/4 inch) across, or about the size of a pencil eraser. *Note: Melanomas can be smaller than this, too.*
Diameter: The mole is larger than 6 millimeters (about 1/4 inch) across, or about the size of a pencil eraser. *Note: Melanomas can be smaller than this, too.*![]()

![]() Evolving: The mole is changing in size, shape, color, elevation, or any other trait; or is new bleeding, itching, or crusting.
Evolving: The mole is changing in size, shape, color, elevation, or any other trait; or is new bleeding, itching, or crusting.
![]() Danger: Melanoma is dangerous because it can spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body, such as lymph nodes, lungs, brain, and liver. Metastatic melanoma is much more difficult to treat and can be fatal.
Danger: Melanoma is dangerous because it can spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body, such as lymph nodes, lungs, brain, and liver. Metastatic melanoma is much more difficult to treat and can be fatal.
![]() Treatment: Treatment options depend on the stage of the melanoma and may include:
Treatment: Treatment options depend on the stage of the melanoma and may include:![]()

![]() Surgical removal
Surgical removal![]()

![]() Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy![]()

![]() Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy![]()

![]() Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy![]()

![]() Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy
![]() Prognosis: The earlier melanoma is detected and treated, the better the chance of a cure. The survival rate is very high for early-stage melanoma that is surgically removed. However, the survival rate decreases significantly as the melanoma spreads.
Prognosis: The earlier melanoma is detected and treated, the better the chance of a cure. The survival rate is very high for early-stage melanoma that is surgically removed. However, the survival rate decreases significantly as the melanoma spreads.
![]() Prevention: The best way to prevent melanoma is to protect your skin from UV radiation by:
Prevention: The best way to prevent melanoma is to protect your skin from UV radiation by:![]()

![]() Seeking shade, especially during peak sun hours (10 AM - 4 PM).
Seeking shade, especially during peak sun hours (10 AM - 4 PM).![]()

![]() Wearing protective clothing, such as long sleeves, pants, and a wide-brimmed hat.
Wearing protective clothing, such as long sleeves, pants, and a wide-brimmed hat.![]()

![]() Using sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, reapplying every two hours, or more often if swimming or sweating.
Using sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, reapplying every two hours, or more often if swimming or sweating.![]()

![]() Avoiding tanning beds and sunlamps.
Avoiding tanning beds and sunlamps.
![]() Self-Exams: Regularly check your skin for any new or changing moles or spots. See a dermatologist for a professional skin exam, especially if you have risk factors for melanoma (fair skin, family history, many moles, history of sunburns).
Self-Exams: Regularly check your skin for any new or changing moles or spots. See a dermatologist for a professional skin exam, especially if you have risk factors for melanoma (fair skin, family history, many moles, history of sunburns).
In Summary:
Melanoma is a serious form of skin cancer that arises from melanocytes. It's primarily caused by UV exposure, but genetic factors also play a role. Early detection and treatment are crucial for a positive outcome. Prevention through sun protection and regular skin exams is essential.
Important Note: This information is for general knowledge only and should not be considered medical advice. If you have any concerns about your skin or a possible mole, please see a dermatologist or other qualified healthcare professional. They can properly diagnose your condition and recommend the best course of treatment.