Neural Tube Defects, Anencephaly
Published: 18 Jun 2025
ICD9: 740.0 ICD10: Q00.0 ICD11: LA00
Neural tube defects (NTDs) are birth defects of the brain, spine, or spinal cord.
They happen when the neural tube, which forms the early brain and spinal cord in the developing embryo, doesn't close completely during pregnancy. Anencephaly is one of the most severe types of neural tube defects.
Here's a breakdown of each part:
![]() Neural Tube Defects (NTDs): As mentioned above, these are birth defects arising from incomplete closure of the neural tube during the first month of pregnancy. The neural tube eventually becomes the brain and spinal cord. Common types of NTDs include:
Neural Tube Defects (NTDs): As mentioned above, these are birth defects arising from incomplete closure of the neural tube during the first month of pregnancy. The neural tube eventually becomes the brain and spinal cord. Common types of NTDs include:![]()

![]() Spina Bifida: Occurs when the spinal cord doesn't close completely. This can cause varying degrees of paralysis, bowel and bladder control problems, and other disabilities. There are different types of spina bifida, ranging in severity.
Spina Bifida: Occurs when the spinal cord doesn't close completely. This can cause varying degrees of paralysis, bowel and bladder control problems, and other disabilities. There are different types of spina bifida, ranging in severity.![]()

![]() Encephalocele: Occurs when part of the brain protrudes through an opening in the skull.
Encephalocele: Occurs when part of the brain protrudes through an opening in the skull.![]()

![]() Anencephaly: As described below.
Anencephaly: As described below.
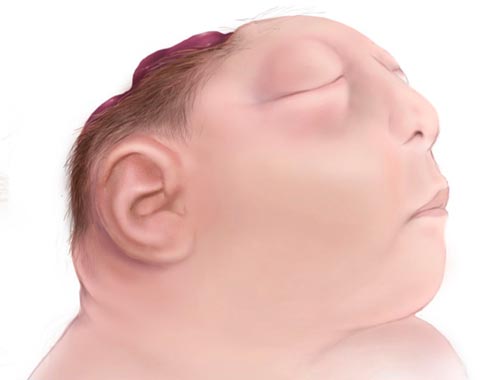
![]() Anencephaly: This is a severe neural tube defect in which a major portion of the brain, skull, and scalp do not develop. Babies born with anencephaly are usually blind, deaf, unconscious, and unable to feel pain.
Anencephaly: This is a severe neural tube defect in which a major portion of the brain, skull, and scalp do not develop. Babies born with anencephaly are usually blind, deaf, unconscious, and unable to feel pain.![]()

![]() Characteristics: Anencephaly is characterized by:
Characteristics: Anencephaly is characterized by:![]()

![]() Absence of a large part of the brain (cerebrum and cerebellum)
Absence of a large part of the brain (cerebrum and cerebellum)![]()

![]() Absence of the skull over the missing brain
Absence of the skull over the missing brain![]()

![]() Remaining brain tissue is often exposed
Remaining brain tissue is often exposed![]()

![]() Survival: Unfortunately, most babies with anencephaly do not survive long after birth. Many die during delivery, and those who are born alive typically live only a few hours or days.
Survival: Unfortunately, most babies with anencephaly do not survive long after birth. Many die during delivery, and those who are born alive typically live only a few hours or days.![]()

![]() Causes: The exact cause of anencephaly is not fully understood, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Factors that increase the risk include:
Causes: The exact cause of anencephaly is not fully understood, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Factors that increase the risk include:![]()

![]() Folic acid deficiency: Insufficient folic acid intake before and during early pregnancy significantly increases the risk.
Folic acid deficiency: Insufficient folic acid intake before and during early pregnancy significantly increases the risk.![]()

![]() Certain medications: Some medications taken during pregnancy have been linked to NTDs.
Certain medications: Some medications taken during pregnancy have been linked to NTDs.![]()

![]() Maternal health conditions: Diabetes, obesity, and certain seizure disorders in the mother can increase the risk.
Maternal health conditions: Diabetes, obesity, and certain seizure disorders in the mother can increase the risk.![]()

![]() Genetic factors: A family history of NTDs can increase the risk.
Genetic factors: A family history of NTDs can increase the risk.![]()

![]() Prevention:
Prevention:![]()

![]() Folic acid supplementation: Taking 400 micrograms of folic acid daily before and during early pregnancy is crucial for preventing NTDs. Some doctors recommend even higher doses for women at higher risk.
Folic acid supplementation: Taking 400 micrograms of folic acid daily before and during early pregnancy is crucial for preventing NTDs. Some doctors recommend even higher doses for women at higher risk.![]()

![]() Prenatal care: Regular prenatal care allows for early detection and monitoring of potential issues.
Prenatal care: Regular prenatal care allows for early detection and monitoring of potential issues.![]()

![]() Avoiding harmful substances: Avoiding alcohol, tobacco, and certain medications during pregnancy is essential.
Avoiding harmful substances: Avoiding alcohol, tobacco, and certain medications during pregnancy is essential.
In summary, anencephaly is a devastating type of neural tube defect where a baby is born without major portions of the brain and skull. It is typically fatal shortly after birth. Folic acid supplementation is the most important preventative measure.
It is important to note that this information is for general knowledge and should not be considered as a substitute for professional medical advice. If you have concerns about neural tube defects or anencephaly, please consult with a healthcare provider. They can provide personalized guidance and address your specific questions.