Peripheral arterial disease Atherosclerosis (Arteriosclerosis)
Published: 18 Jun 2025
ICD9: 443.9 ICD10: I73.9 ICD11: LA90.4
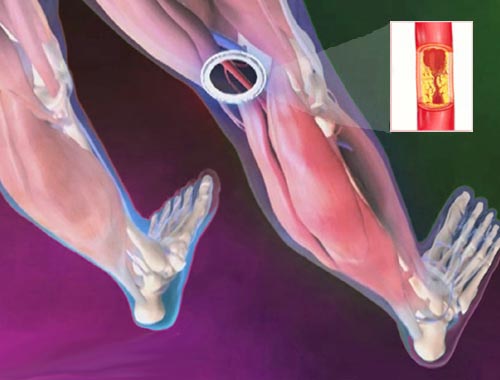
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD), often referred to as peripheral artery disease or just PAD, is a condition where narrowed arteries reduce blood flow to the limbs, usually the legs.
The root cause of most cases of PAD is atherosclerosis (also called arteriosclerosis), a buildup of plaque in the arteries.
Here's a breakdown of the terms and the condition:
![]() Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD):
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD):![]()

![]() Refers to the blockage or narrowing of arteries that carry blood *away* from the heart to other parts of the body, most commonly the legs and feet.
Refers to the blockage or narrowing of arteries that carry blood *away* from the heart to other parts of the body, most commonly the legs and feet.![]()

![]() This reduced blood flow can lead to pain, numbness, and, in severe cases, tissue damage (ulcers, gangrene) and amputation.
This reduced blood flow can lead to pain, numbness, and, in severe cases, tissue damage (ulcers, gangrene) and amputation.
![]() Atherosclerosis (Arteriosclerosis):
Atherosclerosis (Arteriosclerosis):![]()

![]() A process where plaque (made of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances) builds up inside the arteries.
A process where plaque (made of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances) builds up inside the arteries.![]()

![]() This plaque hardens and narrows the arteries, restricting blood flow. While the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, *arteriosclerosis* is a broader term referring to the hardening and thickening of arteries, while *atherosclerosis* is a specific type of arteriosclerosis caused by plaque buildup. In the context of PAD, atherosclerosis is the more precise term.
This plaque hardens and narrows the arteries, restricting blood flow. While the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, *arteriosclerosis* is a broader term referring to the hardening and thickening of arteries, while *atherosclerosis* is a specific type of arteriosclerosis caused by plaque buildup. In the context of PAD, atherosclerosis is the more precise term.
In simpler terms: Imagine your arteries are like pipes carrying blood. Atherosclerosis is like gunk building up inside those pipes, making them narrower and harder for the blood to flow through. PAD is what happens when this gunk restricts blood flow to your legs and feet.
Key points to remember:
![]() PAD is a common condition, especially in older adults.
PAD is a common condition, especially in older adults.
![]() The most common cause is atherosclerosis.
The most common cause is atherosclerosis.
![]() PAD can lead to serious complications if left untreated.
PAD can lead to serious complications if left untreated.
![]() PAD is often underdiagnosed because many people don't experience symptoms early on.
PAD is often underdiagnosed because many people don't experience symptoms early on.
![]() Lifestyle changes and medical treatments can help manage PAD and reduce the risk of complications.
Lifestyle changes and medical treatments can help manage PAD and reduce the risk of complications.
Common Symptoms of PAD:
![]() Claudication: Pain, cramping, or fatigue in the legs or hips that occurs during exercise and is relieved by rest. This is the most common symptom.
Claudication: Pain, cramping, or fatigue in the legs or hips that occurs during exercise and is relieved by rest. This is the most common symptom.
![]() Leg numbness or weakness.
Leg numbness or weakness.
![]() Coldness in the lower leg or foot.
Coldness in the lower leg or foot.
![]() Sores on the toes, feet, or legs that won't heal.
Sores on the toes, feet, or legs that won't heal.
![]() A change in the color of the legs.
A change in the color of the legs.
![]() Hair loss or slower hair growth on the feet and legs.
Hair loss or slower hair growth on the feet and legs.
![]() Slower growth of toenails.
Slower growth of toenails.
![]() Weak or absent pulse in the feet or legs.
Weak or absent pulse in the feet or legs.
![]() Erectile dysfunction (in men).
Erectile dysfunction (in men).
Risk Factors for PAD:
![]() Smoking: The biggest risk factor.
Smoking: The biggest risk factor.
![]() Diabetes
Diabetes
![]() High blood pressure
High blood pressure
![]() High cholesterol
High cholesterol
![]() Older age (especially over 50)
Older age (especially over 50)
![]() Family history of PAD, heart disease, or stroke
Family history of PAD, heart disease, or stroke
![]() Obesity
Obesity
![]() High levels of homocysteine
High levels of homocysteine
If you have any risk factors or symptoms of PAD, it's important to talk to your doctor. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent serious complications.