Salmonella
Published: 18 Jun 2025
ICD9: 003.0 ICD10: A02.9 ICD11: XN0QE
Salmonella is a genus of bacteria that is a common cause of food poisoning (salmonellosis).
Here's a more detailed explanation:
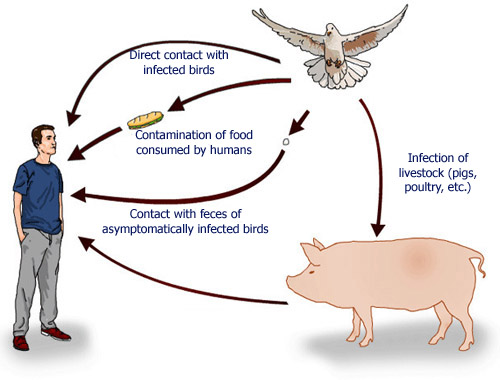
![]() What it is: Salmonella is a group of bacteria that can cause illness in humans and animals. There are many different types (serotypes) of Salmonella.
What it is: Salmonella is a group of bacteria that can cause illness in humans and animals. There are many different types (serotypes) of Salmonella.
![]() How it spreads: It is usually transmitted to humans through contaminated food, such as:
How it spreads: It is usually transmitted to humans through contaminated food, such as:![]()

![]() Raw or undercooked meat, poultry, eggs, and egg products
Raw or undercooked meat, poultry, eggs, and egg products![]()

![]() Unpasteurized milk or juice
Unpasteurized milk or juice![]()

![]() Raw fruits and vegetables
Raw fruits and vegetables![]()

![]() Contaminated water
Contaminated water
![]() Symptoms: Symptoms of Salmonella infection typically include:
Symptoms: Symptoms of Salmonella infection typically include:![]()

![]() Diarrhea
Diarrhea![]()

![]() Fever
Fever![]()

![]() Abdominal cramps
Abdominal cramps![]()

![]() Vomiting
Vomiting![]()

![]() These symptoms usually start 12 to 72 hours after infection.
These symptoms usually start 12 to 72 hours after infection.
![]() Duration: Most people recover within 4 to 7 days without treatment.
Duration: Most people recover within 4 to 7 days without treatment.
![]() Severity: While most cases are mild, Salmonella can cause more serious illness, especially in:
Severity: While most cases are mild, Salmonella can cause more serious illness, especially in:![]()

![]() Young children
Young children![]()

![]() Older adults
Older adults![]()

![]() People with weakened immune systems
People with weakened immune systems![]()

![]() In severe cases, Salmonella can spread from the intestines to the bloodstream and other body sites, requiring hospitalization and antibiotic treatment.
In severe cases, Salmonella can spread from the intestines to the bloodstream and other body sites, requiring hospitalization and antibiotic treatment.
![]() Prevention:
Prevention:![]()

![]() Cook food thoroughly, especially meat, poultry, and eggs.
Cook food thoroughly, especially meat, poultry, and eggs.![]()

![]() Wash hands frequently with soap and water, especially after handling raw food.
Wash hands frequently with soap and water, especially after handling raw food.![]()

![]() Keep raw and cooked foods separate to prevent cross-contamination.
Keep raw and cooked foods separate to prevent cross-contamination.![]()

![]() Refrigerate food promptly.
Refrigerate food promptly.![]()

![]() Avoid unpasteurized milk and juice.
Avoid unpasteurized milk and juice.
It is important to consult a doctor if you suspect you have a Salmonella infection, especially if you have severe symptoms or are in a high-risk group.