Starvation
Published: 18 Jun 2025
ICD9: 994.2 ICD10: T73.0 ICD11: NF07.0
Starvation is a severe deficiency in caloric energy intake, below the level needed to maintain an organism's life.
It's the most extreme form of malnutrition.
Here's a more detailed breakdown:
![]() Cause: Lack of access to food. This can be due to a variety of factors, including poverty, drought, war, political instability, natural disasters, and systemic failures in food distribution.
Cause: Lack of access to food. This can be due to a variety of factors, including poverty, drought, war, political instability, natural disasters, and systemic failures in food distribution.
![]() Physiological Effects: The body begins to break down its own tissues for energy. First, it depletes glycogen stores, then fat, and finally muscle tissue. This leads to:
Physiological Effects: The body begins to break down its own tissues for energy. First, it depletes glycogen stores, then fat, and finally muscle tissue. This leads to:![]()

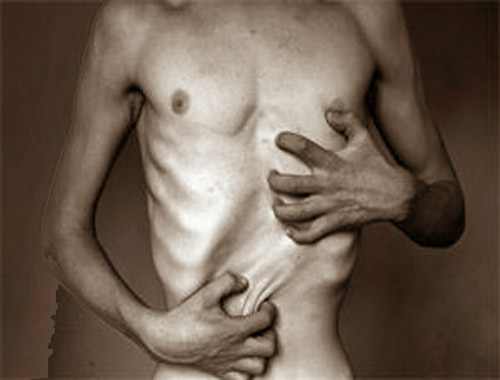
![]() Weight Loss: Dramatic weight loss is a hallmark of starvation.
Weight Loss: Dramatic weight loss is a hallmark of starvation.![]()

![]() Muscle Wasting: Loss of muscle mass leads to weakness and fatigue.
Muscle Wasting: Loss of muscle mass leads to weakness and fatigue.![]()

![]() Organ Damage: As the body breaks down, organs can be damaged. The heart, liver, and kidneys are particularly vulnerable.
Organ Damage: As the body breaks down, organs can be damaged. The heart, liver, and kidneys are particularly vulnerable.![]()

![]() Weakened Immune System: Starvation severely impairs the immune system, making the individual highly susceptible to infections.
Weakened Immune System: Starvation severely impairs the immune system, making the individual highly susceptible to infections.![]()

![]() Metabolic Slowdown: The body tries to conserve energy by slowing down metabolic processes.
Metabolic Slowdown: The body tries to conserve energy by slowing down metabolic processes.![]()

![]() Edema (Swelling): Fluid retention and swelling, especially in the ankles and feet, can occur.
Edema (Swelling): Fluid retention and swelling, especially in the ankles and feet, can occur.![]()

![]() Skin Changes: Skin becomes dry, thin, and prone to lesions.
Skin Changes: Skin becomes dry, thin, and prone to lesions.![]()

![]() Hair Loss: Hair can become brittle and fall out.
Hair Loss: Hair can become brittle and fall out.![]()

![]() Cognitive Impairment: Starvation can affect brain function, leading to confusion, difficulty concentrating, and irritability.
Cognitive Impairment: Starvation can affect brain function, leading to confusion, difficulty concentrating, and irritability.![]()

![]() Death: If left untreated, starvation ultimately leads to death.
Death: If left untreated, starvation ultimately leads to death.
![]() Psychological Effects: Starvation also has profound psychological effects, including:
Psychological Effects: Starvation also has profound psychological effects, including:![]()

![]() Depression: Feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and worthlessness are common.
Depression: Feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and worthlessness are common.![]()

![]() Anxiety: Increased worry and fear.
Anxiety: Increased worry and fear.![]()

![]() Irritability: Being easily agitated or angered.
Irritability: Being easily agitated or angered.![]()

![]() Apathy: Loss of interest in activities and people.
Apathy: Loss of interest in activities and people.![]()

![]() Social Withdrawal: Isolating oneself from others.
Social Withdrawal: Isolating oneself from others.
![]() Rehabilitation: Re-feeding a severely starved person requires careful medical supervision to avoid refeeding syndrome, a potentially fatal metabolic disturbance that can occur when food is reintroduced too quickly.
Rehabilitation: Re-feeding a severely starved person requires careful medical supervision to avoid refeeding syndrome, a potentially fatal metabolic disturbance that can occur when food is reintroduced too quickly.
In summary, starvation is a life-threatening condition that results from a prolonged and severe lack of food. It has devastating physical and psychological consequences and requires immediate medical attention.